Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Static electricity, known as Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), is a familiar occurrence in everyday life, from mundane tasks like unloading clothes from a dryer to walking across a carpet or shaking hands. While these shocks might seem insignificant in certain contexts, they pose significant risks in industries such as data centers, automotive/aerospace manufacturing, and electronic manufacturing.
Dycem® mats are anti static and offer a solution to prevent ESD by actively attracting, collecting, and retaining up to 99.9% of foot and wheel-borne contamination, along with 75% of airborne contamination. This creates an environment free from particles and dust, effectively inhibiting static buildup. With a surface resistivity of 10⁸ ohms, Dycem mats efficiently dissipate static, reducing the likelihood of damage from electrostatic discharge. By facilitating the slow and controlled flow of charges to the ground, these mats prevent discharge to or from human contact.
What is ESD?
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a brief, sudden surge of electric current between two objects that have different electrical charges. Often accompanied by a visible spark, ESD happens when one object becomes positively charged and the other becomes negatively charged. The positively charged object then carries an electrostatic charge, which can be transferred when it comes into contact with another material, resulting in an ESD event.

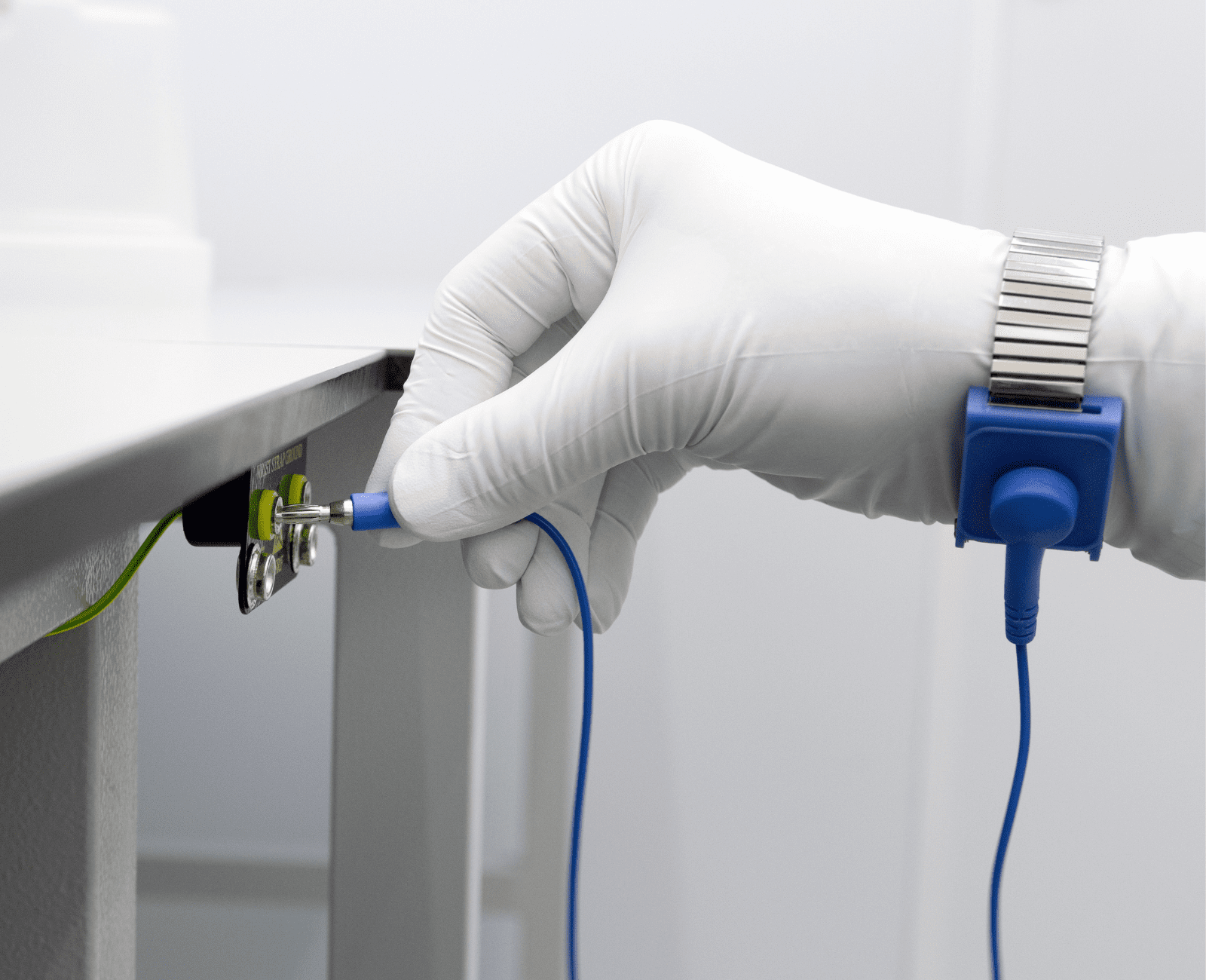

What Causes ESD?
Electrostatic discharge is usually caused by material contact. This is why it happens in everyday occurrences such as walking on carpet and coming into contact with someone. Rapid air movements or circulating fans near electronic equipment can also increase the risk of ESD.
The leading cause of ESD is dust, and keeping critical areas clean can help reduce incidents.
Dangers of ESD in Industrial Environments
ESD can be dangerous for work environments such as data centers, manufacturing, and electronics, causing issues such as:
- Damaging exposed electronic components
- Causing data corruption or loss in electronics
- Acting as an ignition source, leading to fires or explosions
- Interfering with the normal operation of electronic equipment
- Causing physical harm to staff if the discharge comes from a high-voltage environment
Proper training and awareness of ESD is crucial in these environments, alongside an effective ESD control and prevention plan.


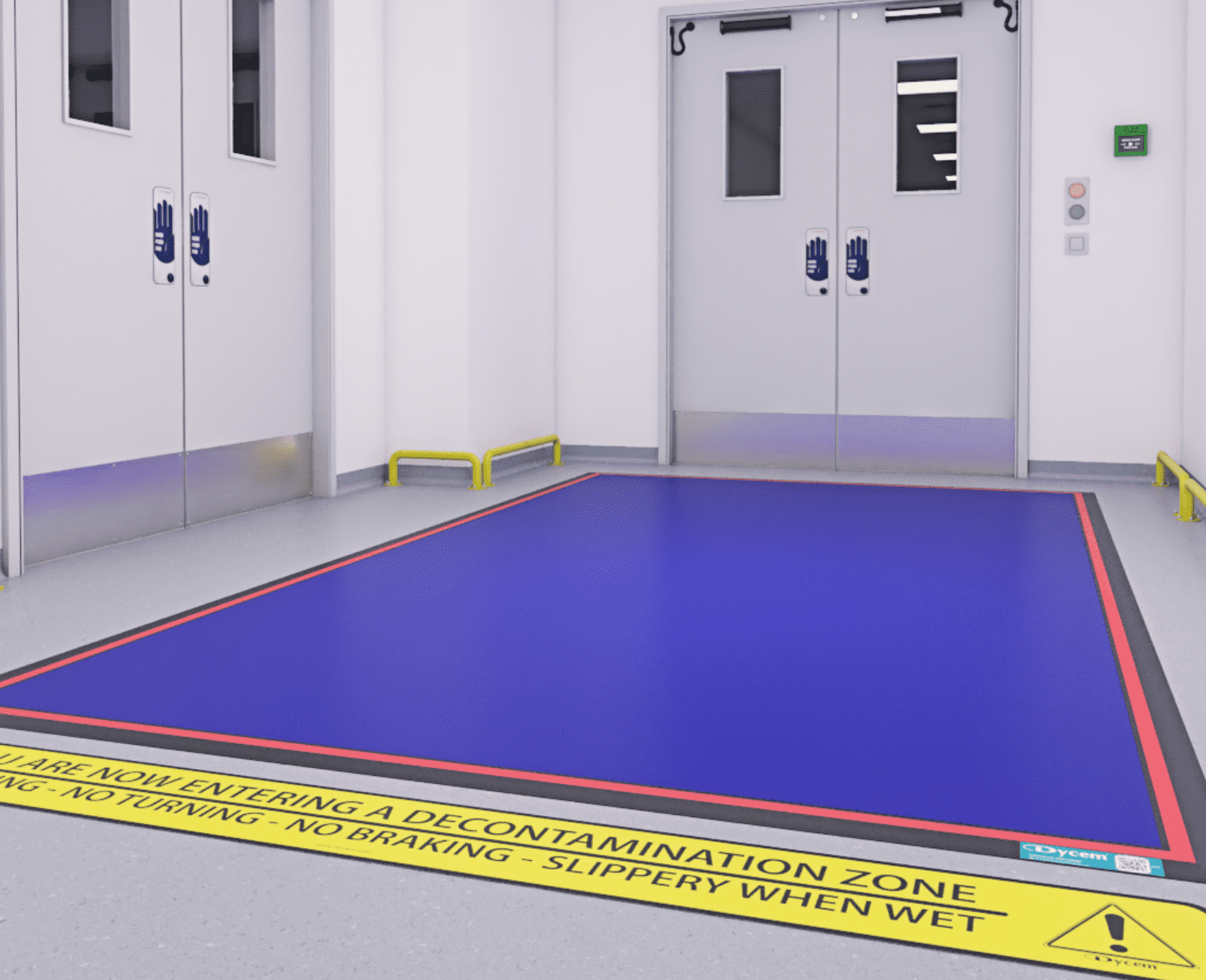

How to Prevent ESD
- Use ESD-safe flooring and mats to cover the floor in critical areas
- Ensure all equipment and furniture are ESD-safe
- Place antistatic mats on desks to protect equipment from ESD
- Remove anything unnecessary from critical areas
- Wear ESD-safe shoes
- Use static-reducing packaging where needed